- Home
- Social Studies
- Jamestown
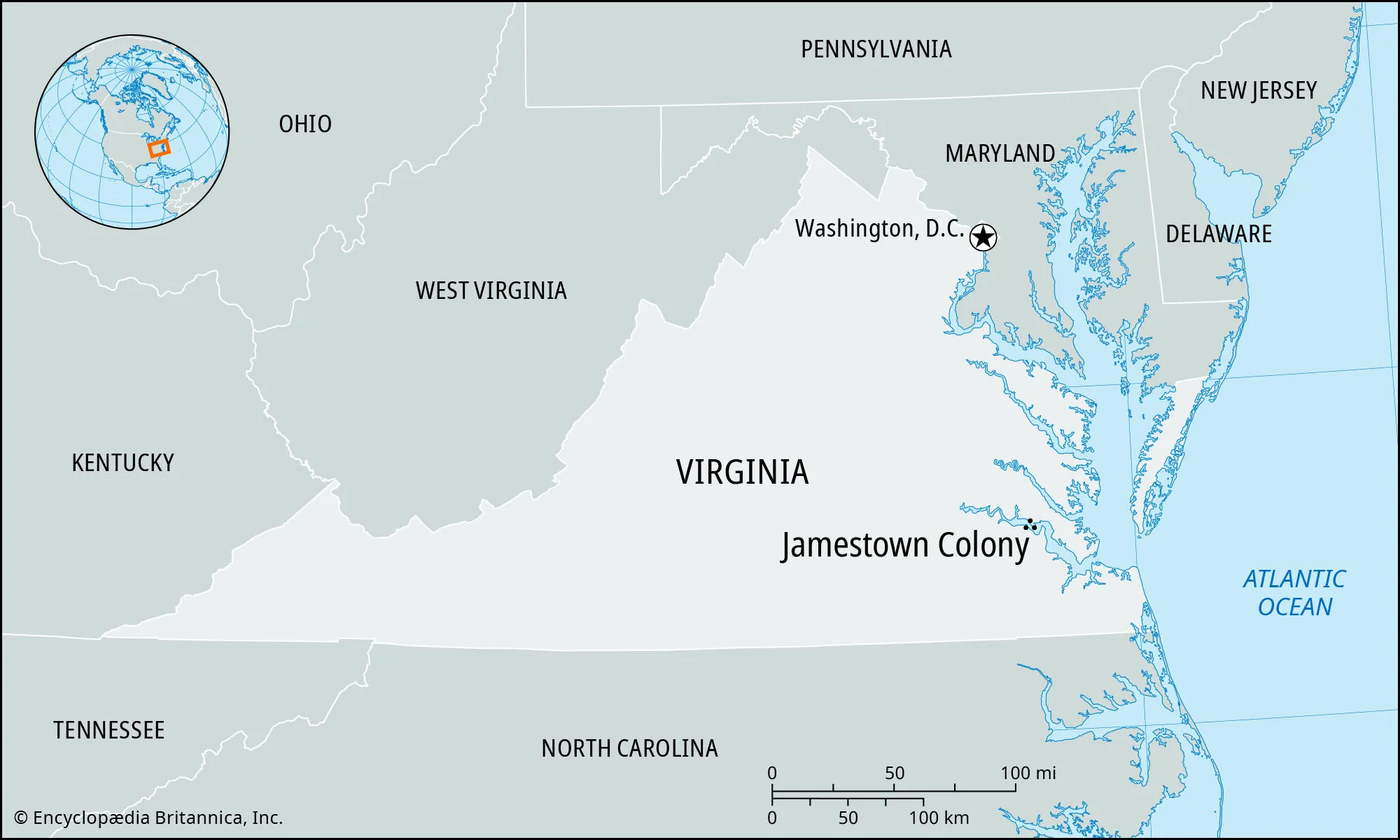
Jamestown - first English settlement
 Jamestown began to thrive and was later the capital of Virginia throughout the seventeenth century.
Jamestown began to thrive and was later the capital of Virginia throughout the seventeenth century.Jamestown was the first permanent English settlement in the New World - a century after the Spaniards had arrived there.
A group of investors and merchants in England formed the London Company for the purpose of colonizing Virginia. King James I granted them the rights, and in December 1606, 104 people left England for North America. They landed in a swamp at Chesapeake Bay in May 1607 and founded the colony they named Jamestown in honor of their king.
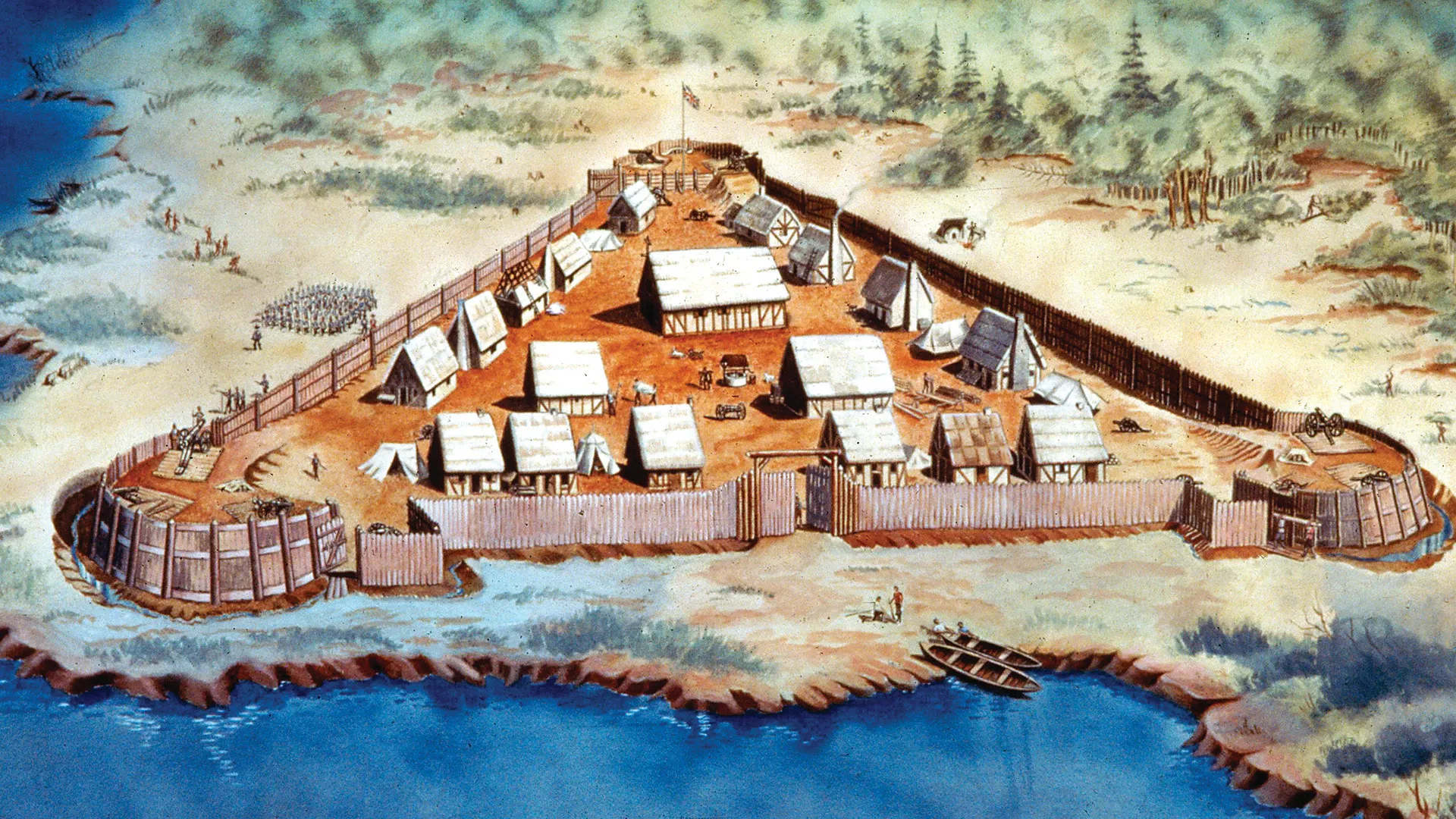
Within days of landing, the colonists were attacked by Powhatan Indians. The newcomers spent the next few weeks working to "beare and plant palisadoes" for a wooden fort. Discovery of the exact location of the first settlement indicates its site was in a secure place, where Spanish ships could not fire point blank into the fort. So, during the first few months, half of the ill-prepared colonists - merchants rather than skilled outdoors-men - were wiped out by a combination of disease, starvation, and the attacks by local Indians.
The London Company sent more men and supplies, but the devastating winter of 1609-1610, called the “starving time,” had few survivors. That year, about 300 settlers crowded into James Fort when the Indians set up a siege, and only 60 settlers came out alive by springtime. Eventually, some years of peace and prosperity followed the 1614 wedding of Pocahontas, the favored daughter of local Chief Powhatan, to tobacco grower John Rolfe. Even so, eight years later, her uncle led a surprise attack in 1622 that killed a third of the colonists and caused the king to take full control of the colony away from the London Company.
Adversity notwithstanding, it was inside this fort that England’s first permanent colony in North America took hold and the seeds for the United States of America grew.
~ did you know ...?
|
Which American city boasts the longest continuous habitation by Europeans? ~ St Augustine, Florida. Founded in 1565 by Spaniard Pedro Menéndez, the settlement was established forty-two years before the English colonized Jamestown. |
What is the oldest state capital city in the United States? ~ New Mexico became a state as recently as 1912, but its capital city was first settled more than three centuries earlier, in 1609. |
Jamestown Entrepreneurship
In Renaissance England, wealthy merchants were eager to find investment opportunities, so they established several companies to trade in various parts of the world. Each company was made up of investors, known as "adventurers", who purchased shares of company stock. The Crown granted a charter to each company with a monopoly to explore, settle, or trade with a particular region of the world. Profits were shared among the investors according to the amount of stock that each owned. More than 6,300 Englishmen invested in joint-stock companies between 1585 and 1630, trading in Russia, Turkey, Africa, the East Indies, the Mediterranean, and North America.
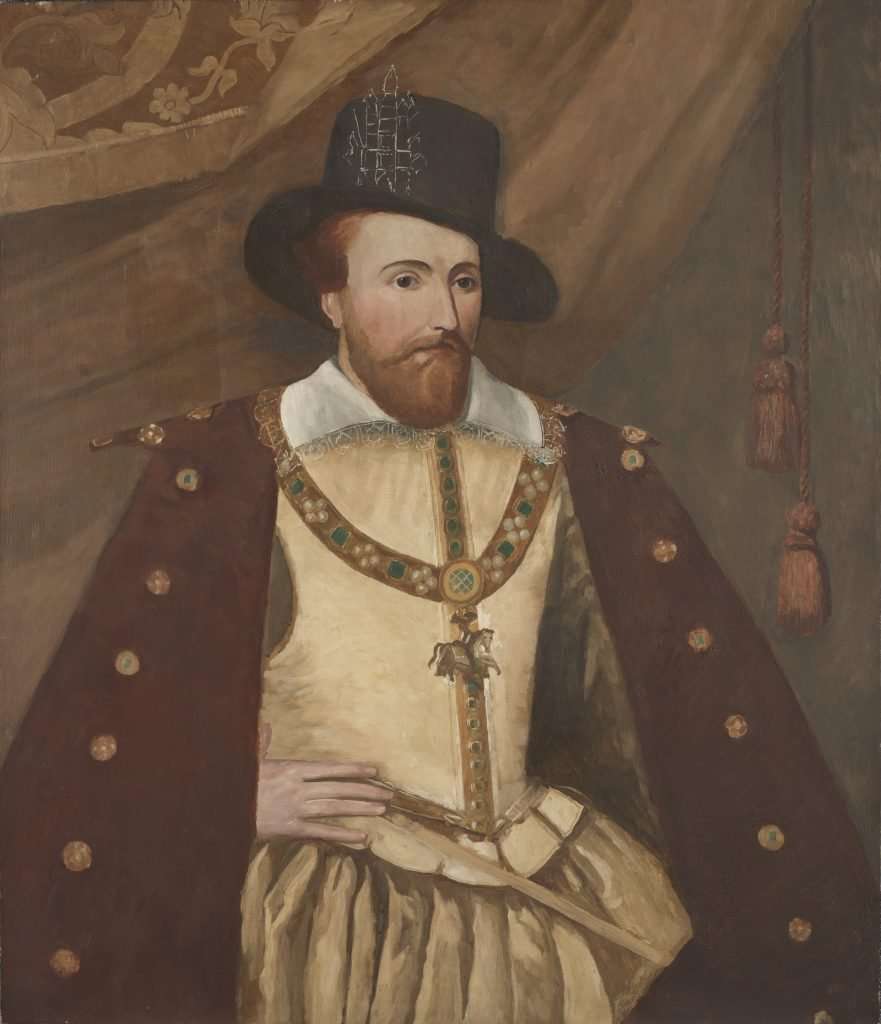 James I - King of England when wealthy English merchants provided the vast capital needed to establish an American colony.
James I - King of England when wealthy English merchants provided the vast capital needed to establish an American colony.King James I issued charters for two companies in 1606. The first, the London Company, covered what is now Maryland, Virginia, and Carolina. The second company, the Plymouth Company was empowered to settle far north, encompassing what is present-day Pennsylvania, New Jersey, New York, and New England. The London Company was set up by entrepreneurs, while the Plymouth company sought religious freedom. But only the London Company succeeded in establishing a permanent colony as the Plymouth colony was abandoned in 1608 due to the many difficulties of frontier life: hunger, Indian attacks, leadership crises, etc.
Investors in the London Company hoped to profit from the natural resources of the New World. The business model of the company was the settlement of the Virginia colony, supported by a labor force of voluntary transportees under the customary indenture system.
In exchange for 7 years of labor for the company, the company provided passage, food, protection, and land ownership (if the worker survived). In addition to surviving, the early colonists were expected to make a profit for the owners of the London Company. Although the settlers were disappointed that gold did not wash up on the beach and gems did not grow in the trees, they realized there was great potential for a wealth of other kinds in their new home. The individuals who ventured to the New World were motivated by a chance at prosperity: to improve their economic and social standing.
By 1619 a system of indentured service was fully developed in the colony.The company paid all the costs of establishing each colony, and in return controlled all land and resources there, requiring all settlers to work for the company.

Yet, Jamestown and the London Company struggled financially - especially with labor shortages. So, in order to keep colonists there, the London Company allowed them to own land, which attracted many newcomers to the area. Its profits improved after sweeter strains of tobacco than the native variety were cultivated and successfully exported from Virginia as a cash crop beginning in 1612. Then, the, home government passed a law that prohibited the shipments of goods from the colonies directly to foreign markets; shipments were required to pass through England before going to for sale, whereby the crown could levy taxes.
By 1621, the company was in trouble; unpaid dividends and increased use of lotteries had made future investors wary. The company debt was now over £9,000. In March 1622, the company's and the colony's situation went from dire to disastrous when, during the Indian massacre of 1622, the Powhatan confederacy killed one-quarter of the European population of the Virginia colony.
In 1624, to address leadership crises and financial issues King James I changed the status of Virginia, taking control of it as a royal colony to be administered by a governor appointed by the King. Jamestown began to thrive and was later the capital of Virginia throughout the seventeenth century.
Jamestown Charters
After so many failed colonizing attempts in the 16th century such as the Roanoke Colony, and with the ascension of King James to the throne of England on 24 March 1603, the effort to colonize was renewed.
The Charter of 1606
The 1606 grants by James I to the London and Plymouth companies. The areas were granted to both companies on the condition that neither found a settlement within 100 miles (160 km) of the other. The First Virginia Charter (or London Company Charter) established provisions for the governance of the colony. It was to be governed by a colonial council, which proved ineffective.
The Charter of 1609
In
1609, the Virginia Company received its Second Charter, which allowed
the company to choose its new governor from among its shareholders.
Investment boomed as the company launched an intensive recruitment
campaign. Over 600 colonists set sail for Virginia between March 1608 and march 1609

The Charter of 1612
The third Virginia Charter or Charter of 1612, was essentially the same as the Charter of 1609, with the difference being territorial jurisdiction, expanding it to the Atlantic Islands like Bermuda and from "sea to sea."
The Great Charter
The Great Charter was an ordinance and constitution that proceeded from a set of instructions issued in 1618 to the governor and the Council of Virginia known as An Ordinance and Constitution of the Virginia Company in England on 24 July 1621. This document replaced military law with common law, and provided for land ownership for settlers living in the colony. It is also of great significance for it provides governance independent of the Crown.
Collapse and dissolution
When the Crown and company officials proposed a fourth charter, severely reducing the company's ability to make decisions in the governing of Virginia, subscribers rejected it.
After 1620, with growing demand for tobacco on the continent, the company arranged to sell Virginia tobacco in the Netherlands, but the next year and despite company pleas to maintain the privilege of freedom of trade, the Privy Council forbade the export of any product of Virginia to a foreign country until the commodities had been landed in England, and English duties had been paid. Worried Virginians were hardly reassured by the advice of pragmatic Treasurer Edwin Sandys who warned that the company "cannot wish you to rely on anything but yourselves."
Native
American relationships
The instructions issued to Sir Thomas Gates, on 20 November 1608, called for a forcible conversion of Native Americans to Anglicanism and their subordination to the colonial administration.
In 1609, the company issued instructions to settlers to kidnap Native American children so as to educate them with English values and religion. These instructions also sanctioned attacking the Iniocasoockes, the cultural leaders of the local Powhatans.
Only after Thomas West, 3rd Baron De La Warr arrived in 1610, was the company able to commence a war against the Powhatan with the First Anglo Powhatan War. De La Warr was replaced by Sir Thomas Dale, who continued the war, which continued until a truce was made with the marriage of Pocahontas to John Rolfe in 1614.
The military offensive was accompanied by a propaganda war: Alderman Robert Johnson published Nova Britannia, in 1609, which compared Native Americans to wild animals -"heardes of deere in a forest." While it did portray the Powhatan as peace-loving, it threatened to deal with any who resisted conversion to Anglicanism as enemies of their country.
Self Rule
Perhaps most important of all is that Jamestown had the first government with representation. Instead of following the dictates of a governor, the Jamestown colonists had some degree of self-rule. In the 1620s, representative government took hold, and the town grew into “James Cittie.” This principle became the fundamental idea of all future English colonies and was, ultimately, the very idea that led to the American Revolution.
Virginia, where Jamestown was founded, was the first of the 13 English colonies.
The 12 other colonies were Connecticut, Delaware, Georgia, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and South Carolina.
|
Un siglo después de la llegada de los españoles al Nuevo Mundo, los ingleses establecieron su primera colonia permanente. Un grupo de invesionistas y negociantes de Inglaterra formaron la Compañia de Londres con la intención de colonizar Virginia - lo que entonces se consideraba la mayor parte de América del Norte. Desembarcaron en un pantano de la bahia de Chesapeake en 1607 y establecieron la colonia que llamaron Jamestown en honor a su rey. A lo largo, los colonos de Jamestown tenían cierto grado de autogobierno. Esto principio llegó a ser una idea fundamental en lo sucesivo para todas las colonias inglesas, y eventualmente condujo a la Guerra de la Independencia. |
Click here for more about Jamestown ....
Okay, so now I've put on some ads from Amazon - from which I may earn a few cents. (2025)



